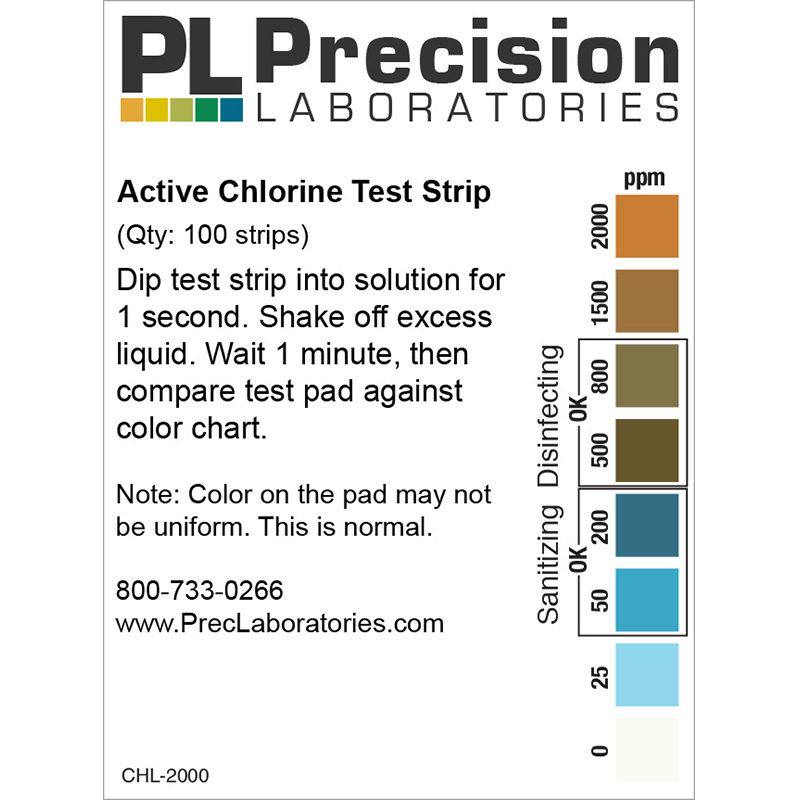
The Active Chlorine test strip tests levels of free chlorine in a solution. The increments are 0, 25, 50, 200, 500, 800, 1500, 2000ppm. The color chart has obvious color changes from blue to brown to orange. This test strip is very easy to use, and gives results in just seconds. The Active Chlorine test strips can be used in facilities where food preparation areas, equipment, and general disinfection are more strictly controlled. Specifically, this product was developed for use in daycare centers and senior homes, where a disinfection level slightly higher than that available using our High Level Chlorine strip is required.
Active Chlorine Test Strip, 2000ppm
Active Chlorine Test Strip, 2000ppm
- Dip the Active Chlorine test strip into solution for 1 second.
- Remove strip and shake off excess water.
- After 1 minute, compare pad against color chart. (Note: color on the pad may not be uniform; this is normal.)

CHL2000; CHL-2000; CHL-2000-1V-100
Product Specs
| SKU: | CHL-2000-1V-100 |
|---|---|
| Strip Quantity: | 100 strips |
| Vial Dimensions: | 1.125″ (D) x 3.375″ (H) [29mm (D) x 86mm (H)] |
| Strip Dimensions: | 2.5" (L) x .1875" (W) [64mm (L) x 5mm (W)] |
| Weight: | 0.09 lbs [42.5 g] (100-strip vial) |
| Other: | Stored in a flip-top vial with built-in desiccant liner. |
| Shelf-Life: | 2 Years |
| Label: | Customizable water-resistant label |
Product Documentation
SDS
Fact Sheet
Videos
What is the recommended concentration of bleach for dangerous pathogens?
Chlorine bleach at concentrations of at least 1000ppm is an effective germicide for dangerous pathogens such as MRSA (Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus), VRE (Vancomycin Resistent Enterococci) and Clostridium difficile. The High Level Chlorine ( 0-1,000ppm) test strip is suitable for use with Deardorff-Fitzsimmons ACTIVATE disinfectant (5.25% Sodium Hypochlorite solution) for in vitro control of such dangerous pathogens.
However, the removal of free chlorine by organic contamination (blood/feces) can seriously reduce the sanitizing effects of chlorine cleaning solutions. To ensure the 1000ppm minimum strength for adequate disinfection, much higher initial concentrations, up to 10,000ppm (1%) chlorine levels are recommended to counteract this and can be check with our Extra High Level Chlorine (0-10,000ppm) test strip.
How do I determine the recommended bleach concentration for a certain product?
To determine the recommended bleach concentration for your application, locate the EPA registration number on your product label. Visit the EPA’s website, and enter the EPA Registration Number, then click Search. You should see the details about the product, and beneath that, a PDF bearing the date that this product was registered by the EPA (if there is a list, the PDF at the top of the list should show the most recent approval). Click on that most recently-approved PDF. The PDF should come up on your screen. Scroll down to the section that shows the directions for using the product as a sanitizer or disinfectant. Follow the directions listed for your intended use.
How do I select the correct chlorine test strip?
Chlorine is one of the most popular chemicals for cleaning, sanitizing, and disinfecting. Two common examples will help illustrate this. Swimming pools are often treated with chlorine chemicals. In this application, the amount of chlorine needed is low, typically only 1-3ppm chlorine. On the other hand, disinfection of daycare and hospital facilities requires a much higher chlorine level, typically 600-1200ppm. In both examples, the 0-200ppm chlorine test paper is not the best choice. Precision Laboratories manufactures a whole range of chlorine test strips. Please consult our product listing for the chlorine test strip that best matches your application.
What is the ideal pH of an available chlorine solution?
All available chlorine has some biocide strength, although hypochlorous acid is a far stronger biocide than hypochlorite ion or the chloramines. In solutions at pH of 5-7, hypochlorous acid is the most prevalent species. For this reason, most sanitizing solutions will work best in the neutral to slightly acidic pH range.
What is the difference between free available, combined available, and total available chlorine?
When chlorine gas (Cl2) or bleach (sodium hypochlorite or NaOCl) is added to water the result is the formation of hypochlorous acid (HClO).
Cl2 + H2O -> HOCl + H+ + Cl-
NaOCl +H2O -> HOCl + Na+ + OH-
Depending on the pH of the solution the hypochlorous acid exists in solution as either hypochlorous acid (HClO) or hypochlorite ion (OCl-).
HOCl OCl- + H+
Free available chlorine refers to the amount of hypochlorous acid AND hypochlorite ions present.
Combined (or bound) available chlorine arises when nitrogen (usually in the form of ammonia) is present to form what are called chloramines (mono-, di-, and trichloramines are possible).
Total available chlorine is the sum of the free available chlorine and the combined available chlorine.